Single Agent vs Multi Agent in AI- Comparison with Use Cases
Everyone knows that a group of brilliant minds is more powerful than one brilliant mind when it comes to solving a problem.
But is this the case with every problem? Or do different problems require a different number of brains?
Confused?
Let me tell you, nowadays, AI system design is an ongoing topic; everyone is talking about Agentic AI Tools, multimodal AI, MCP, and so on….
And under agentic AI come two terms: single-agent AI and multi-agent AI. Both are suitable for different types of problems.
In this blog, we’ll learn in detail about both single-agent vs multi-agent in AI in clear and simple language. We will discuss when each one should be used, some real-world examples, and which is right for your AI project.
What is a Single AI Agent?
A single AI agent is an autonomous system that thinks and acts on its own without help from other agents. It does everything independently, like it senses its environment, makes decisions, and completes tasks within one focused area.
You can think of it like a skilled expert who is really good at one job.
Single-agent AI works best in predictable and limited environments, such as a navigation tool that picks the fastest delivery route, a voice assistant that schedules reminders, or a movie recommendation engine.
In simple terms, it’s like someone learns only one route to a destination. If that route changes even a little, the person gets stuck and can’t move forward.
You can say, any conversational AI platform works with a single-agent AI system like Botpress.
What is a Multi-Agent AI System?
A multi-agent AI system brings several AI agents together to work toward the same goal. Each agent has a specific role and skill, and they coordinate to solve tasks that are too large or complex for a single agent to manage alone.
For example, it’s like several people know different routes to the same place. If one person gets stuck, they can ask the others for help, share directions, and together they find the best path to continue.
CrewAI can be considered as an example of multi-agent AI that has a team of multiple agents that work together and compete tasks.
Single Agent vs Multi Agent in AI: Complete Side-by-Side Comparison
| Factors | Single Agent AI | Multi-Agent AI System |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | One model makes all decisions independently. | Multiple agents collaborate and share decisions. |
| Task Type | Simple, predictable, single-flow tasks. | Complex, multi-step, interconnected tasks. |
| Speed vs Scalability | Fast but slows with task growth. | Slightly slower but highly scalable. |
| Learning Style | Learns only from its own experiences. | Shared learning across multiple agents. |
| Error Handling | Failure in unknown or dynamic situations. | Other agents cover, fix, or take over tasks. |
| Integration | Easy plug-and-play setup. | Requires coordinated communication logic. |
| Cost | Low initial cost; expensive to scale later. | High initial cost; cheaper expansion over time. |
| Use Cases | Chatbots, routing, recommendations. | Logistics, automation, enterprise workflows. |
Single Agent vs Multi Agent – Key Differences
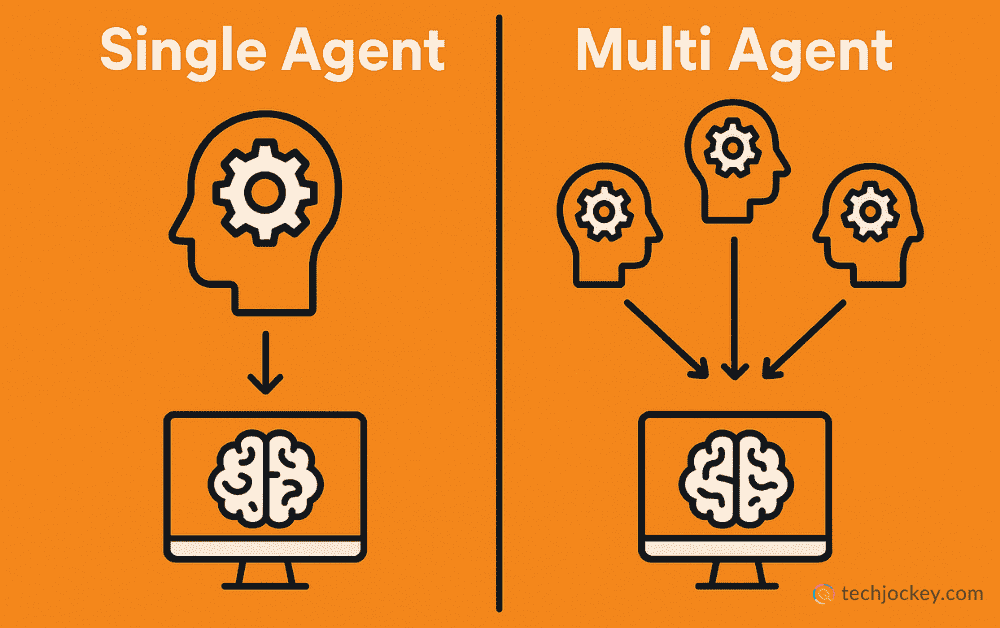
Let’s break down the differences between single-agent vs. multi-agent one by one.
How Are Decisions Made?
A single-agent system works with one smart unit that understands the problem, takes action, and gives the result from start to finish. It thinks alone, plans alone, and works alone, which makes it good for simple, clear tasks.
On the other hand, a multi-agent AI system works like a team of multiple skilled brains, with each agent doing a different job. These agents talk to each other, share information, split tasks, check each other’s work, and work together to reach the final goal, making it good for tough situations where a single agent might have trouble or fail.
How Tasks Are Managed ?
In single agent AI, the task is usually straightly aligned and easy to predict, like answering a question, finding information, making a suggestion, or creating content. Because the work is limited, the system stays easy to build and easy to control.
In multi-agent AI, tasks have many layers and are connected. One agent may look at data, another one may plan the next step, another may do the work, and one may check quality. The complexity of tasks is not a problem, it’s what allows multi-agent systems to reach goals that a single agent cannot.
Is speed prioritized or scalability?
A single-agent model focuses on speed, and it’s efficient in handling requests on its own. There is no need for talking or planning with other agents, so answers can be very fast when the problem is small. However, as the tasks scale, the agent becomes slow.
A multi-agent setup may take a bit longer because agents need to work together, but it scales much better. More agents can be added to share work, help more users, handle new tasks, or work at the same time. In this way, the performance gets better as the system grows rather than getting worse.
How do They Learn?
With a Single Agent, learning stays separate. The agent gets better with practice or past experiences, but only based on its own interactions and the training data fed. Its growth is limited by one model.
In multi-agent AI, learning can be shared. One agent’s experience can be shared with others, and agents can watch each other’s choices, give feedback, and improve work together. This leads to faster growth, better accuracy over time, and more reliable thinking.
What happens if something goes wrong?
In a single-agent setup, if the agent faces an unknown situation, missing information, or a skill gap, the entire task may fail because there is no other agent to help or check the choice.
In a multi-agent system, if one agent fails, another often handles it. Agents can check, fix, watch, or even take over for each other during work. This creates a built-in safety feature that improves stability in high-risk or real-time settings.
Here multi-agent system is more beneficial than a single AI agent.
How easy is integration?
A single agent is easy to add to existing systems. It works like a plug-in or tool that does one job well and doesn’t need a lot of structure around it, which makes it good for quick setup.
A multi-agent setup needs planning and teamwork logic because multiple agents need to talk, work together, and share information. The building effort is higher at the start but pays off when long-term growth and automation are important.
How Much Do They Cost?
A single-agent solution is usually cheaper to build at first because you only have one model to train, set up, and keep running. However, growing it later may lead to higher system changes and ongoing work.
A multi-agent system needs more budget at the start, but once the agents and the talking system are ready, improving or growing the system becomes much cheaper over time. You can simply add new agents instead of rebuilding everything.
Single Agent vs Multi Agent Examples
Example 1- Customer Support Automation
Imagine a company that wants complete customer support automation.
A single-agent chatbot can handle frequently asked questions easily, but a multi-agent system can provide a more complete experience.
In a multi-agent environment, one agent could handle customer messages, another could check product availability, another could process refund requests, and another could update customer records. The multi-agent approach leads to faster, more accurate support, and customers receive better service without human intervention.
Example 2- Logistics and Delivery
Let’s take an example of a logistics company that delivers products across multiple cities. A single agent can plan the shortest delivery route, which is useful, but it cannot manage inventory, driver schedules, roadblocks, or warehouse operations.
A multi-agent AI system can split these responsibilities across specialized agents, enabling real-time coordination among vehicles, drivers, traffic conditions, and warehouse robots. As a result, deliveries become faster, cheaper, and more error-free.
These simple stories show why the single-agent vs multi-agent environment in AI comparison matters in real life; the scale and nature of the task define the best approach.
Why Don’t We Always Pick Multi-Agent Systems?
Even though multi-agent systems seem more powerful, they are not always the right choice. A multi-agent AI system needs strong communication rules, reliable error-handling, correct task sharing, and high engineering maturity. Finding problems becomes harder because issues may not come from one agent but from many agents’ interactions. The starting cost is higher, and projects need more time and knowledge.
This is why many companies build an AI system using a single agent first, test if it works and performs well, and then move to a multi-agent setup if dynamic steps need to be added. This approach keeps the budget under control and reduces risk.
The Rise of Hybrid Agentic AI Systems
A growing trend in the AI world is the hybrid approach, where both single and multi-agent structures are mixed. In this setup, a central brain acts as a single high-level decision-maker, while multiple small agents do tasks on their own.
Amazon uses this model in its warehouse automation system: a central AI manages stock and planning, while teams of local robotic agents pick, pack, and move products on the floor.
This hybrid strategy balances efficiency, autonomy, and scalability and is increasingly regarded as the ideal long-term solution for enterprise-grade AI deployments.
Final Thoughts
When you know what your requirements are, development time is less, and the environment is predictable, then a single AI agent is a viable and affordable option.
But when your project requires complex reasoning, real-time synchronization, scalability, or collaboration with multiple systems, a multi-agent AI system will provide better long-term results.
The goal is not to follow trends but to design an AI architecture that matches the problem. Many successful AI products start with a single-agent setup and evolve into multi-agent systems as they grow. What matters most is alignment between your AI goals, business needs, and the environment where the system will operate.
Mehlika Bathla is a passionate content writer who turns complex tech ideas into simple words. For over 4 years in the tech industry, she has crafted helpful content like technical documentation, user guides, UX content, website content, social media copies, and SEO-driven blogs. She is highly skilled in... Read more