What is Manufacturing Execution System? Features, Working, and Types Explained

Are you facing production delays, rising defect rates, or not able to have real-time visibility into your manufacturing process?
If yes, then not only do you face this! Many manufacturers often struggle with disconnected systems, manual reporting, and slow workflows. These all problems could lead to higher costs and missed deadlines. That’s where MES software could be of use.
In fact, a study says, By using MES software, one can reduce cycle times up to 30%, cut defect rates by 25-40% and boost equipment effectiveness by approximately 33%.
This blog post is all about MES software, its architecture, benefits, and implementation. By the end of the blog, you will have a complete understanding of what is MES software in manufacturing.
What Is MES Software?
MES full form in engineering is Manufacturing Execution System. Its definition in one simple sentence is that it’s a specialized manufacturing execution system that manages and monitors production processes on the factory floor.
You can say it as a connection between ERP and actual machine-level operations. While ERP is to know what needs to be produced, MES, on the other hand, describes how and when of the production process.
MES software’s job is to capture data from machines, operators, and sensors. It gives complete visibility to manufacturers about:
- Production scheduling
- Work-in-progress (WIP) tracking
- Quality control and compliance
- Resource utilization
- Machine performance and downtime
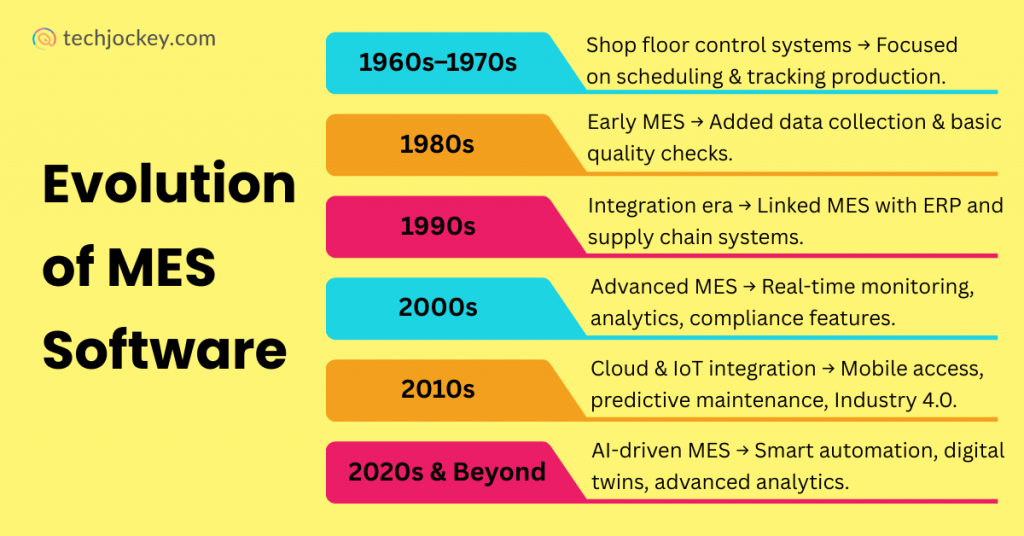
Top MES Features That Boost Manufacturing Efficiency
A good manufacturing execution system software doesn’t just monitor but also manages everything.
Here are the key features of an MES software:
- Helps in Production Scheduling & Dispatching: MES software helps you to plan, assign, and track production orders so that you can meet the production deadlines.
- Collects Data in Real Time: It captures data from production machines, sensors, and operators for complete shop-floor visibility.
- Track the Work Progress: It lets you monitor each and every stage of production, whether it is raw material usage, workers’ performance, or if anything is required more.
- Helps in Quality Management: It detects defects in any product at an early stage, so that you can fix them to manage compliance standards and maintain consistent product quality.
- Generate Reports for Better Analysis: Reporting is the best part of an MES software, as manufacturers can generate insights into machine utilization, downtime, cycle times, and operator efficiency.
- Helps in Inventory & Resource Management: It lets you track materials, tools, and worker availability to avoid delays in production.
- Provides Full Trace of Every Stage: You can record the full production history of each product. It makes audits easy.
- Integrates with ERP and IoT: You can integrate MES software easily with shop-floor systems and smart devices for end-to-end visibility.
How Many Types Of Manufacturing Execution System Are There?
MES software is different for different industries and production models. The following are the categories of MES software:
- Discrete Manufacturing MES: This type of MES software is designed for industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics. It provides high-precision tracking of individual units or batches.
- Process Manufacturing MES: This MES software manages continuous processes and helps ensure safety standards in industries like chemical, food, and pharmaceutical.
- Hybrid MES: It’s a conglomeration of discrete and process MES. It’s commonly used in the packaging and consumer goods industries where both unit-based and process-based production exist.
- Cloud-Based MES: As the name suggests, this type of MES software is hosted on the cloud. Manufacturers can access data in real time from anywhere, making production easy on the go. It is scalable, budget-effective, and best for companies with multiple locations.
- On-Premise MES: This manufacturing execution software is installed locally on a company’s servers. Manufacturers can have high customization and control. It is mostly preferred by highly regulated industries.
How Does An Manufacturing Execution System Work?
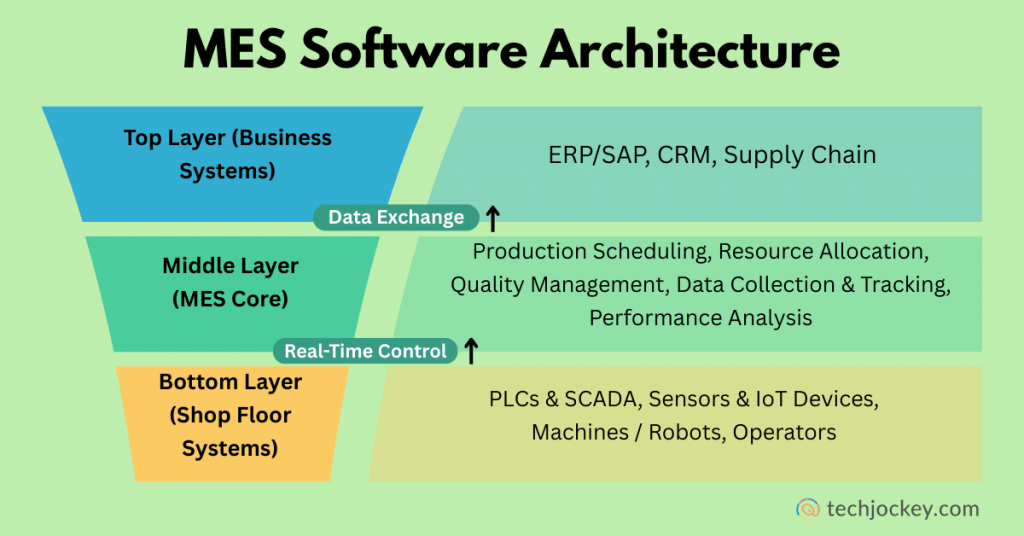
Let’s now explain the working of an MES system in manufacturing.
- Data Collection Layer: MES collects data on machines, IoT sensors, PLCs (programmable logic controllers), and manual inputs. The layer gives a real-time status of production.
- Processing & Control Layer: The system converts raw data into information to be acted upon. It keeps track of WIP, machine activity, labor productivity, and inventory.
- Application Layer: This layer offers functionalities such as quality control, resource management, and scheduling. It integrates with the ERP system in order to match production to business objectives.
- User Interface Layer: At this layer, supervisors, operators, or managers can access dashboards, alerts, reports, etc., to ensure quick decision-making.
- Integration Layer: MES can connect with ERPs and the shop floor systems. It ensures that production is in line with sales orders, planning, and customer demand.
Top MES Software in 2026
Although there are several in the market, here’s a list of MES software that are widely used by manufacturers:
- Siemens Opcenter is one of the best options used in large companies. It provides scalability and high automation integration. Its prices are not available publicly but some sources say that it begin around $1000 or more, depending on the implementation.
- Rockwell Automation FactoryTalk is popular in discrete manufacturing to perform monitoring and scheduling in real-time and is often priced around $35,000-$60,000/year based on the features.
- Dassault Systèmes DELMIA Apriso offers visibility into multi-plant operations worldwide and can be used in complex supply chains. The pricing of this software is based on the customer’s requirements.
- Lastly, GE Digital Proficy is known for having IoT and analytics integration, which is why it is mostly adopted by hybrid manufacturers. Some sources say that its subscription costs start around $5,800 per month.
How To Implement MES System?
Above, we have discussed some MES software, but the question is how to implement them in the workflow?
Here are a few steps to do this job:
- Firstly, find out what challenges your current process is facing. It could be downtime reduction, quality challenges, etc.
- Now, check out your existing systems, like ERP or CRM. Do they have the capabilities to integrate with the MES software?
- Now, choose any of the MES software you think will suit your production workflow.
- Break the rollout into phases, start with a pilot project before scaling to the entire plant.
- If you previously had any production data, import it and set up connections with machines, sensors, and manufacturing ERP software.
- Training your employees like operators, supervisors and managers is the most important step.
- Lastly, continuously evaluate performance metrics and update the system for maximum efficiency.
Manufacturing Execution System (MES) vs ERP: Key Differences
Many manufacturers confuse MES with ERP, but while they complement each other, they serve different purposes.
| Functionalities | MES (Manufacturing Execution System) | ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) |
|---|---|---|
| What it does? | Shop-floor operations and production control | Business planning and resource allocation |
| Features | Manages WIP, quality, machine data, and scheduling | Covers finance, HR, supply chain, procurement |
| What’s the Timeframe? | Real-time, short-term execution | Long-term planning and forecasting |
| Who can use it? | Plant operators, production managers | Business leaders, finance, HR, supply chain teams |
| Can Integrate? | Acts as a bridge between machines and ERP | Provides enterprise-wide decision-making |
Manufacturing Execution System (MES) Software Trends
Production companies are transforming the way they keep track of their work. And this is what is going on now:
- Moving to the Cloud: An increasing number of companies are abandoning their legacy computer systems and transitioning to cloud systems. It costs less to begin and is easy to expand.
- Smart Technology Takes Over: The factory systems now use AI to predict when the machines may need repairs, organize the work, and prevent issues before they occur.
- Everything Connects: Sensors and smart equipment transmit real-time data to MES and make the factory a smarter place to work.
- Virtual Twins: Companies make digital replicas of their machines and processes to test and optimize production.
- Work From Anywhere: Managers can now check on their factories from their phones or home computers, day or night.
- Custom Solutions: Industries such as pharma, auto, and food and beverages have their own custom-made MES tools to address rigid regulations and exclusive requirements.
The Big Picture, These MES systems not just track, now they help companies work smarter and compete better in the modern world.
Final Thoughts
The demands of the day are hard on factories – produce things faster, cheaper, and better than ever. That is where manufacturing software comes into play. With these MES systems, you can trace all the activities taking place in your factory, from raw materials to finished products. They bring together all your machines, employees, and computers so that no one is left in the dark on the happenings around.
These systems are becoming smarter every day with the use of cloud computing, AI, and automation. The time to get the right factory management system is not something that you can delay. It has become necessary to remain competitive.
FAQs
Are MES and ERP the same?
No, they are different. ERP determines what and when to produce, but MES determines how it is produced in real time on the shop floor.
How much does a MES system cost?
An MES system varies in cost depending on the vendor, size, and customization. Small setups will cost prices starting at $50,000, and large enterprises will require several million.
Is SAP a MES system?
No, SAP is an ERP software that has a few MES modules. A complete MES system offers a greater level of shop-floor control and visibility.
What training is needed for MES?
Dashboards, reports, and system workflows are normally training areas required by operators, supervisors, and managers. The vendor or in-house training may depend on the complexity of the MES.
What is the difference between CRM and MES?
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) involves customer interactions and sales, and MES is concerned with production and manufacturing. The two are dissimilar but can be combined to achieve end-to-end visibility.
Mehlika Bathla is a passionate content writer who turns complex tech ideas into simple words. For over 4 years in the tech industry, she has crafted helpful content like technical documentation, user guides, UX content, website content, social media copies, and SEO-driven blogs. She is highly skilled in... Read more