7 Types of ITR Forms You Should Know Before Filing Your Return
Filing your Income Tax Return is not just a formality; your compliance depends on it. In the FY 2023-2024, over 86 million people filed ITR, and for FY 2024-2025, the number is expected to cross 91 million.
So, if you are in this list, the question is which type of ITR should you file? Which ITR form should you use?
Since the source of income of every taxpayer is different, there are various ITR forms introduced by the government. The different categories are for salaried individuals, business owners, organizations, and even trusts/NGOs.
Why Filing ITR is Important?
- Submitting your Income Tax Return (ITR) is part and parcel of your financial records. Here’s why it is so important to file it:
- It allows you to remain within the tax regulations and avoid fines for late or missing filing.
- It is also with the help of ITR that you can claim back any excessive tax deducted to avoid any money loss.
- In addition to compliance, it is also important in financial planning since ITR documents can be necessary in receiving a loan, in applying for a visa, or even as proof of income during significant transactions.
- Filing also enables you to carry forward certain losses to offset against future gains, which will lower your tax payment.
- Most importantly, it develops your financial credibility and keeps you on the frontline in the growth of the nation through taxes.
Let me explain all the types of ITR forms in detail to be used in FY 2024-25.
Types of ITR Forms
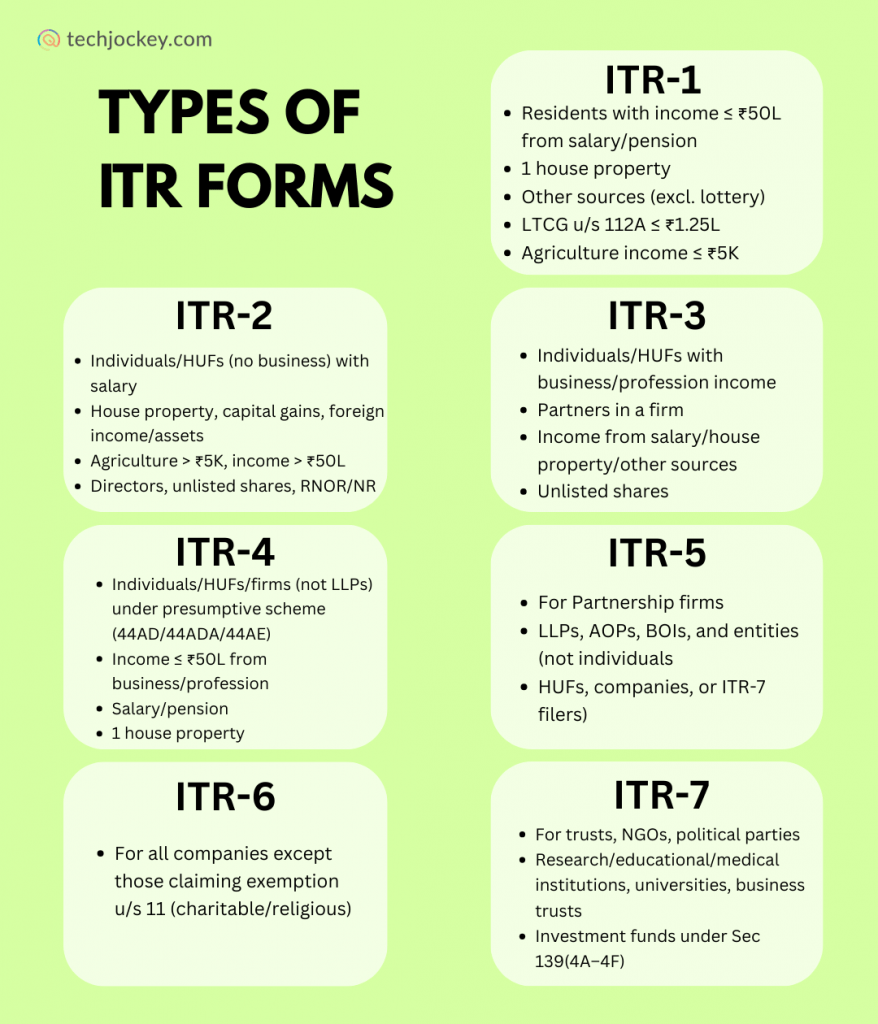
ITR-1 (Sahaj)
ITR-1, which is called Sahaj, is a form to be used by resident individuals whose total income is less than or equal to INR 50 lakh. It is the simplest form, which is often used by salaried employees and pensioners.
This ITR form is excluded for the categories – HUFs or companies.
Who can use this form?
- Individuals with income from a salary or a pension
- Income from one house property (excluding cases with carried forward losses)
- Income from other sources (excluding lottery winnings and race horses)
- Long-term capital gains under Section 112A up to INR 1.25 lakh
- Agricultural income up to INR 5,000
ITR-2
ITR-2 is another type of ITR form and is meant for individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) who do not earn from business or profession. It is generally used by people with multiple income sources, like capital gains or foreign income.
Who can use this form?
- Individuals/HUFs with income from salary, pension, house property, or other sources
- Those with capital gains
- Directors in a company or investors in unlisted equity shares
- Residents, RNORs, and Non-residents with foreign income or assets
- Agricultural income above INR 5,000
- Anyone clubbing the income of a spouse, child, etc., when it falls under these categories
ITR-3
ITR-3 applies to individuals and HUFs that generate income from a business. It
also includes partners in firms and those that are not entitled to ITR-1,
ITR-2, and ITR-4.
Who can use this form?
- Individuals/HUFs earning from business or professional activities
- Partners in a firm (share of profit, interest, commission)
- Those with income from salary, house property, or other sources, along with
business/profession income - Investors in unlisted equity shares
ITR-4 (Sugam)
One other form of ITR on the list is ITR-4. Also referred to as Sugam, it applies to individuals, HUFs, and firms (except those LLPs which choose the presumptive taxation regime in Sections 44AD, 44ADA, or 44AE). The small businesses, freelancers, and professionals primarily use this form.
Who can use this form?
- Taxpayers with a total income of up to INR 50 lakh.
- Those with presumptive business or professional income.
- Income from salary/pension, one house property, or other sources (excluding lottery/race horses).
- Freelancers or small traders with turnover under INR 2 crore (under presumptive scheme).
ITR-5
ITR-5 applies to entities other than individuals, HUFs, or companies. It is mainly used by partnerships and other associations.
Who can use this form?
- Partnership firms
- Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs)
- Associations of Persons (AOPs) and Bodies of Individuals (BOIs)
- Other similar entities are not required to file ITR-7
ITR-6
ITR-6 is a type of ITR form applies to companies except those that have claimed exemption under Section 11 (charitable or religious trusts).
Who can use this form?
- Domestic and foreign companies are not exempted under Section 11
- Companies earning income from business, profession, or other sources
ITR-7
ITR-7 is another type of ITR form and is primarily applicable to individuals/companies that are required to file ITR under Sections 139(4A–4F).
It primarily addresses trusts, NGOs and charitable, political, and research institutions.
Who can use this form?
- Trusts and institutions under Section 139(4A)
- Political parties under Section 139(4B)
- Research associations, news agencies, educational or medical institutions under Section 139(4C)
- Universities, colleges, and business trusts under Sections 139(4D–4E)
- Investment funds under Section 139(4F)
Additional Types of ITR Forms Required
There are a few supporting forms and documents that are required, along with choosing the right type of ITR form.
1. Form 16: This document is required by salaried people to file ITR. It is issued by your employer annually, and it has two parts.
Part A: This part shows the TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) deducted from your salary.
Part B: It contains details of your total income, deductions claimed, and the estimated tax payable.
2. Form 26AS
Form 26AS is a consolidated statement that shows all TDS deducted on your behalf during the year. It also covers the income on which TDS was charged, specific financial transactions (SFT), and even turnover according to GST records. It is like a cross-checking tool for the taxpayers prior to filing returns.
3. Form 10-IEA
This form is required if you want to opt for or switch out of the new tax regime.
4. Form 10B
This type of ITR form is applicable for trusts and institutions to claim exemptions and benefits.
How to File ITR Online?
Before you go for filing ITR, there are a few documents you need to keep ready. These are PAN card, Aadhaar card, Form 16/26AS, your bank details, interest certificates, any donation receipts, and investment proofs.
You can either file directly through the government portal or use an income tax software to simplify the process.
Here’s how you can file ITR online through the government portal:
- Log in to the government official website using your PAN details and password.
- Select the assessment year 2025-26 for filing ITR for the financial year 2024-25.
- Select your filing status, whether you are an individual, HUF, or come in any other category.
- Pick the correct type of ITR form to file that matches your income sources.
- Add the reason for filing ITR. Some of them could be taxable income above the exemption limit, mandatory under law, etc.
- Now, enter income and deductions. Most of the details are pre-filled on the portal, like salary, TDS, bank name, etc. But there is a need to verify these details and correct them if required.
- Review, pay any pending tax, and submit your return.
- Verify within 30 days via Aadhaar OTP, Net Banking, EVC, or by sending the signed ITR-V to CPC Bengaluru.
Important: The last date to file ITR for Financial Year 2024-25 is 15th September 2025. This date has been extended from July 31, 2025. In case you missed filing till the due date, you have to pay late fees afterwards.
Conclusion
The right type of ITR form and its submission at the right time guarantee that you are tax compliant. As over 91 million ITRs are expected to be submitted during AY 2025-26, taxpayers must keep a check on the proper ITR forms, supporting documents, and deadlines to submit tax returns.
Be it if you are self-employed, an organization, salaried, or a trust, you all have a certain type of ITR form that fits you. Filing properly not only will help you to avoid penalties, but it will also enhance your financial credibility.
Mehlika Bathla is a passionate content writer who turns complex tech ideas into simple words. For over 4 years in the tech industry, she has crafted helpful content like technical documentation, user guides, UX content, website content, social media copies, and SEO-driven blogs. She is highly skilled in... Read more