The world’s networks transmit billions of data packets every second, with each one bearing fragments of your emails, passwords, financial information, business secrets, and whatnot. That is an insane amount of online traffic, and the big question it raises is: How safe is your information?
Well, if recent reports are any indication, more than 60% of organizations have fallen victim to some sort of network monitoring or data packet interception within the past year alone. The tool behind most of these? Packet sniffing in cybersecurity.
Packet sniffing is a cyber tactic used to intercept and examine data packets in transit. While it serves as a tool of great significance for IT teams, it is also increasingly taken advantage of by cybercriminals, meaning to steal private data.
Understanding packet sniffing’s meaning and how you can defend against it is thus essential, especially in the digital world we live in. Let’s get into it, shall we?
Packet sniffing in cybersecurity, put simply, is the act of capturing and analyzing data packets traveling through a network. Think of these packets as envelopes consisting of your personal information and carrying them from your device to their final, intended destination. A packet sniffer, as such, is a postal worker who discreetly opens and reads these envelopes as they go by.
Now that you know packet sniffing meaning, also note that it can be done for various reasons. While IT teams can use it for troubleshooting or performance monitoring, cybercriminals, conversely, can use it to steal sensitive information.
SentinelOne
Starting Price
Price on Request
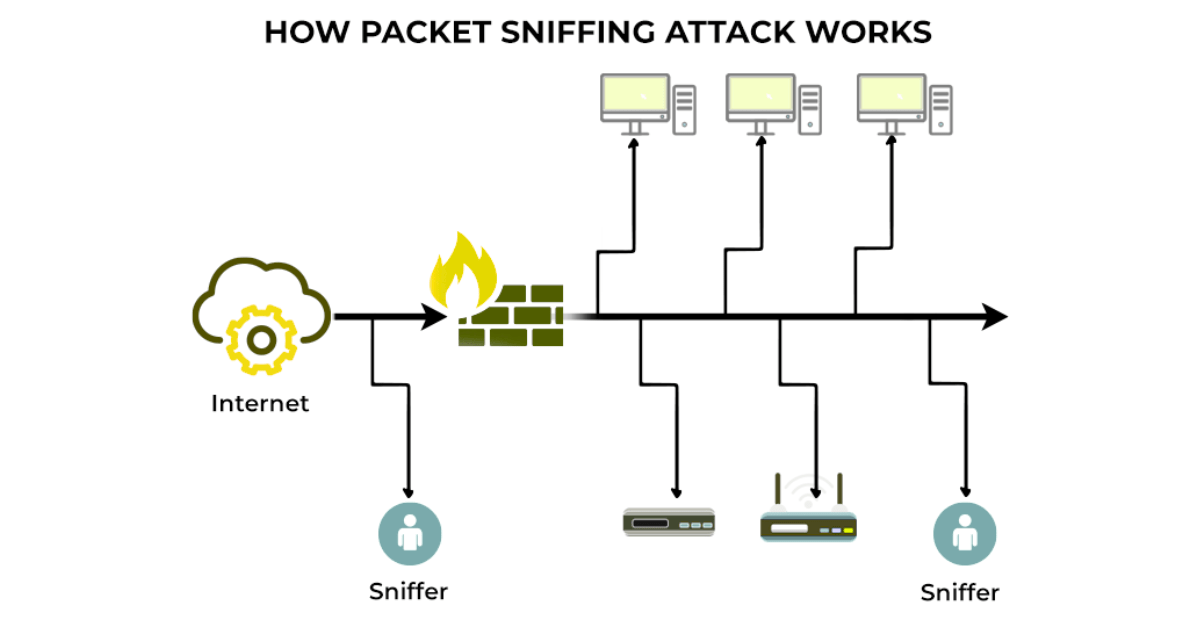
Data that is sent through the internet gets divided into small packets. These packets house the information of the sender and the receiver, and the data itself. Normally, devices only process packets meant for them. However, a device running a network packet sniffer can capture all packets passing through its network segment.
Here’s how the process works…
This can be done both on wired networks (using an Ethernet packet sniffer or LAN packet sniffer) and wireless networks (using a WiFi sniffer).
Packet sniffing in cyber security can be broken down into several distinct types, each with unique techniques and risks…
1. Passive Packet Sniffing
Passive packet sniffing is when the packet sniffer avoids interfering with any data but quietly monitors all network traffic. This works best on networks using hubs, where all devices see every packet.
2. Active Packet Sniffing
In this, the attacker adds extra traffic or tampers with network protocols (such as ARP spoofing) to cause switches to broadcast packets to all devices on the network. This allows the attacker to intercept data even on modern switched networks, which are typically designed to limit packet visibility to the intended recipient.
One example of active packet sniffing would be a hacker making use of ARP poisoning on a corporate LAN. This, to trick the switch into sending all traffic through their machine for interception.
Active packet sniffing is a common tactic in man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
3. Filtered Packet Sniffing
The network packet sniffer, in filtered sniffing, is configured to intercept a particular type of packet, say, packets of a particular IP address, port, or protocol. This assists hackers in targeting sensitive information like login credentials or transactions.
4. Unfiltered Packet Sniffing
For unfiltered packet sniffing, on the contrary, the network packet sniffer picks up all packets without distinction, making a total record of the network traffic. Though data-intensive, this approach can produce unexpected outcomes when used in the process of forensic investigation.
Singularity Control
Starting Price
$ 79.99
5. Protocol-Specific Sniffing
The traffic sniffer, in this case, targets only those network protocols that pass data in plain text or can be easily exploited. These include protocols like FTP, Telnet, HTTP, DNS, SMTP, etc. The best example of it would be the use of a Wi-Fi sniffer to intercept unencrypted FTP credentials at a public hotspot.
6. Application-Level Sniffing
The traffic sniffer is customized to target the data in particular applications, like email clients, browsers, or messaging apps, and reassemble entire conversations or document transfers. A LAN packet sniffer, for instance, can be used to reassemble chat messages sent using an internal messaging application over an unsecured network.
7. Hardware vs. Software Sniffers
Hardware sniffers are specialized devices connected to the network, which are commonly used by practitioners to perform in-depth diagnostics or by attackers to carry out covert long-term monitoring. Software sniffers, on the contrary, are applications such as Wireshark or tcpdump, which are installed on computers to capture and analyze packets.
Zaperon Zero Trust
Starting Price
Price on Request
8. LAN Sniffer vs. Wi-Fi Sniffer
While a LAN packet sniffer is used on wired networks to sniff traffic in a local area network, a Wi-Fi sniffer, on the other hand, is used on wireless networks to sniff information over the air. They are particularly dangerous when used over a public Wi-Fi, where encryption is sometimes lenient or non-existent.
Detecting packet sniffing in cybersecurity is challenging because packet sniffing tools are designed to be stealthy. However, there are sundry warning signs and detection tactics that you can use to remain wary at all times. Some of them are mentioned below for your convenience…
Packet sniffing in cybersecurity can be mitigated with a layered defence strategy. Here are the most effective methods you can use to attain the same…
NeuShield Data Sentinel
Starting Price
Price on Request
Conclusion
Packet sniffing in cybersecurity is a constantly evolving threat. Attackers today make use of a variety of sniffing techniques to intercept and analyze network traffic. Things definitely get riskier when unsecured or public networks are involved, but even private networks can become dangerous if used without proper defences.
Understanding what packet sniffing is and how these attacks work is thus the first step in defending yourself. So, stay alert for signs of trouble, use encryption, and let a good cybersecurity software guide the way for you. Call the Techjockey product team today if you need any help with the lattermost.
Healthcare often feels complicated, slow, and scattered across many disconnected systems. Patients carry reports, repeat… Read More
The present-day workplace hardly bears any resemblance to the traditional setups of bygone eras. Diverse… Read More
Fruitful interaction in the modern market requires rapid speed, rich context, and genuine empathy. Shoppers… Read More
Staying compliant is one of the most important parts of running business. Labor laws,… Read More
Managing a website today is very different than it was ten years ago. Back then,… Read More
With IT infrastructure, nowadays, spread across cloud platforms, various systems, third-party services, and tools that… Read More