Cloud Computing vs Edge Computing: Key Differences, Pros, and Use Cases
is thusIn this ever-evolving digital world, businesses are always on the lookout for means to manage, assess, and store the vast volumes of data generated by connected devices and applications. This need has given rise to an important battle, namely, cloud computing vs edge computing.
Knowing the difference between cloud computing and edge computing is thus essential for businesses that wish to optimize their performance, cost, and user experience.
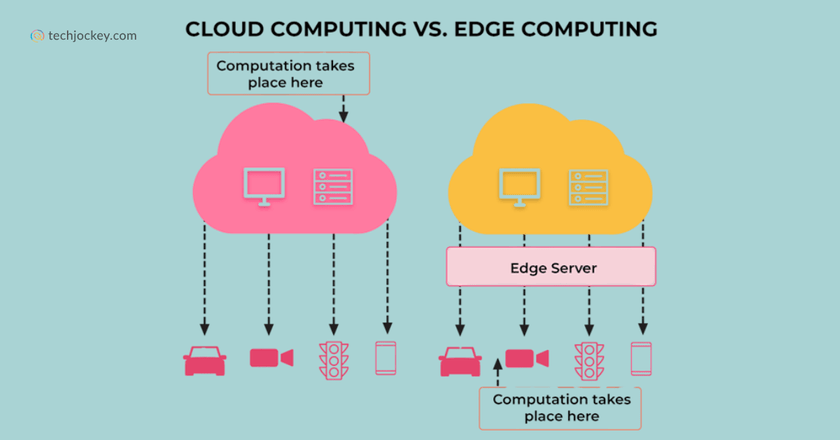
To give you a brief overview, cloud computing computes data in centralized servers and is suitable for extensive storage and analytics. Edge computing, on the other hand, processes data close to the source, which allows efficient responses for real-time applications. If you want an in-depth analysis of the two, go on reading…
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the process of delivering computing services, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics, on the internet through centralized data centers managed by providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
These cloud services provide the user with a means to access resources on demand and scale up and down as needed, without the hassle of managing physical infrastructure.
Key Features of Cloud Computing
- Centralized Infrastructure: Data and applications are hosted in remote data centers managed by cloud service providers.
- Scalability: Resources can be easily ramped up in light of changing needs.
- Remote Accessibility: Users have the ability to access cloud services from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Elasticity: Companies are only required to pay for resources they consume, making it a cost-efficient endeavour.
- Self-Service Provisioning: End users can provision resources on demand without engaging IT.
- Broad Network Access: Services are accessible through the net across various kinds of devices.
- Multi-Tenancy & Resource Pooling: The same infrastructure is used in a secure manner by several customers.

Microsoft Azure
Starting Price
Price on Request
Advantages of Cloud Computing
- Cost Efficiency: It minimizes capital expenditure on hardware and maintenance, helping you shift to a pay-as-you-go model.
- Business Continuity: Data is stored and retrievable in the case of disaster, facilitating strong disaster recovery strategies.
- Agility & Speed: Quick rollout of applications and services accelerates time to market and innovation.
- Automatic Updates: Cloud management services make certain that users have access to the latest features and security patches at all times.
- Environmental Sustainability: Shared infrastructure optimizes resource consumption while minimizing carbon footprint.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
- Latency: Since data is required to travel to and from distant data centers, it can lead to delays, making cloud computing unfit for real-time applications.
- Bandwidth Dependency: It requires reliable, high-speed internet connectivity at all times.
- Data Privacy & Security: Sensitive information is stored away from the location, which is a cause for concern in terms of compliance and control.
- Potential Downtime: Despite being rare, outages in cloud computing platforms can affect critical applications in access.
Common Use Cases for Cloud Computing
- Data storage and backup
- Application hosting, for example, SaaS
- Big data analytics
- Development and testing environments
- Disaster recovery
- Content delivery via cloud networking services
For more information on cloud computing, refer to our blog on What is Cloud Computing (with Examples) and put your doubts to rest.

NetApp Cloud
Starting Price
Price on Request
What is Edge Computing?
Instead of relying on centralized cloud data centers, edge computing processes data closer to its point of origin, such as IoT devices, sensors, or local edge servers. By taking computation to the edge of the network, it decreases latency, improves real-time processing of data, and minimizes bandwidth requirements.
Key Features of Edge Computing
- Decentralized Processing: Data is analyzed and acted on at the point of origin.
- Low Latency: Edge processing allows for quicker response times that are necessary for time-sensitive processes.
- Enhanced Privacy: Sensitive data stays on the local device, enhancing privacy and security.
- Reduced Bandwidth Usage: Only important data is sent to the cloud, which reduces network traffic and expenses.
- Reliability: Edge systems operate even when connectivity with the cloud is lost.

Akamai Cloud
Starting Price
Price on Request
Advantages of Edge Computing
- Real-Time Processing: It is perfect for operations that need instant feedback, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and augmented realities.
- Improved Security: Since edge computing keeps data local, the chances of a data breach are reduced significantly.
- Cost Savings: Eliminates the need for high-speed access to the cloud and, at the same time, reduces the cost of data transmission.
- Scalability: Supports large-scale IoT deployment without overburdening central infrastructure.
- Operational Continuity: Systems can function smoothly in connectivity-challenged environments.
Disadvantages of Edge Computing
- Limited Resources: Edge devices usually have limited processing capability and storage than that of cloud data centers.
- Management Complexity: Deploying, updating, and securing distributed edge devices can be a daunting endeavour.
- Scalability Constraints: Though the edge can scale locally, expanding across many sites could necessitate a lot of coordination.
- Data Fragmentation: It gets tough to access data for centralized analytics or backup.
Common Use Cases for Edge Computing
- Autonomous vehicles and drones
- Smart cities and infrastructure, including traffic lights, surveillance, etc.
- Industrial automation and robotics
- Healthcare devices and remote monitoring
- Real-time gaming and AR/VR applications

Amazon AWS
Starting Price
₹ 1.00 excl. GST
Cloud Computing vs Edge Computing: Key Differences
Understanding the difference between cloud computing and edge computing is key to making informed technology decisions today. Some of the most important distinctions in this debate of cloud computing vs edge computing are thus mentioned below for your convenience…

1. Location of Data Processing
Cloud computing uses centralized data centers, which are sometimes away from the data source. Edge computing, on the other hand, performs computing on data at or near its source, be it on local devices, edge servers, or gateways.
2. Latency & Real-Time Responsiveness
Cloud computing can cause a great deal of latency owing to the distance that the data in question needs to travel. This makes it an inappropriate choice for applications that need instant feedback. Edge computing, on the other hand, reduces latency by processing data at a local level, making it possible for a program to respond to critical applications in a timely and effective manner.
3. Bandwidth Usage & Network Dependency
Cloud computing is a bandwidth hog as enormous amounts of data are carried from the cloud and sent back. Edge computing, conversely, reduces the need for bandwidth by processing and filtering data locally and only sending important information to the cloud.
4. Scalability & Resource Availability
Cloud computing platforms provide indefinite scalability and are therefore perfect for workloads with variable or unpredictable needs. The scalability of edge computing, on the contrary, is limited by the number and capability of local devices. It can, however, scale horizontally by deploying more edge nodes.

Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Starting Price
Price on Request
5. Reliability & Operational Continuity
Cloud computing relies on stable and high-speed internet connectivity. In case of connection loss, access to cloud-hosted applications and data can be disrupted.
Edge computing, on the other hand, functions independently of the cloud, so the work continues even if there are network outages. This makes edge computing significant for mission-critical systems.
6. Security, Privacy & Compliance
Cloud services use the most vigorous security protocols, but since the data leaves its origin, concerns of privacy and compliance are bound to arise, even more so when it involves sensitive or regulated information.
Guarding data on the edge, contrarily, entails processing and storing sensitive information locally. This minimizes the risks of exposure and facilitates adherence to the data sovereignty laws. However, the distributed nature of edge computing creates new security threats as every edge device needs protection.
7. Management Complexity
Cloud management services simplify centralized resource management, monitoring, and updates. Edge computing involves the management of a network of distributed devices, which may be challenging and expensive, particularly as the number of edge nodes increases.
8. Energy Consumption & Environmental Impact
Cloud data centers are designed to be energy-efficient, yet the transfer of a huge amount of data ends up using more energy. On the flip side, edge computing minimizes the cost of energy used for data transmission; however, it still needs to regulate the use of power within numerous distributed devices.

Teradata VantageCloud
Starting Price
$ 9000.00
9. Application Development & Integration
Cloud computing takes advantage of APIs and automation to make application deployment and scaling easy. The development of edge computing, by contrast, is more complicated because of various hardware and environments involved, but it tends to combine better with legacy systems, especially in industrial contexts.
10. Disaster Recovery & Backup
Cloud computing comes equipped with disaster recovery, backup, and redundancy to deliver business continuity. Backup and recovery in edge computing, however, are required to be handled across various sites and devices, making it more difficult in comparison.
11. Cost Structure
Cloud computing is based on a pay-as-you-go model that is largely cost-effective, except in situations involving bandwidth-heavy, latency-sensitive applications.
Edge computing, contrarily, can be more expensive to implement, but its operating expenses are low due to fewer data transmission and central storage requirements.
Choosing the Right Approach: Cloud, Edge, or Both?
When faced with the choice between cloud computing vs edge computing, take a stock of your business needs, application requirements, and operational context. Having done so, make a choice…
Choose cloud computing when…
- You need to store and process large volumes of data
- Applications are not latency-sensitive
- Scalability and flexibility are top priorities
- Centralized management and backup are essential
- Use cases include big data analytics, SaaS, and disaster recovery
Or choose edge computing when…
- Real-time processing and low latency are critical
- Applications must operate reliably in remote or connectivity-challenged locations
- You need to minimize bandwidth usage and data transmission costs
- Data privacy and local compliance are important
- Use cases include IoT, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial automation
In many scenarios, a hybrid approach to edge computing and cloud computing produces top results. For instance, edge devices can perform local processing of data for instant response and then send the aggregated insights to the cloud for long-term storage, analytics, and integration with other cloud networking services.

Tencent Cloud
Starting Price
Price on Request
Conclusion
The argument on cloud computing vs edge computing is not about which is better, but about which is more appropriate for a given task. For businesses intent on creating agile, efficient, and future-ready digital infrastructure, knowing the difference between cloud computing and edge computing, and when to use each, will be pivotal.
A quick tip-off, take it or leave it, but with digital transformation speeding up and the number of connected devices increasing, organizations would actively resort to blending the best of both paradigms, and that is what you should do too. Thank you later!
Yashika Aneja is a Senior Content Writer at Techjockey, with over 5 years of experience in content creation and management. From writing about normal everyday affairs to profound fact-based stories on wide-ranging themes, including environment, technology, education, politics, social media, travel, lifestyle so on and so forth, she... Read more