What is GSTR – 9C and How to File It?

GST registration is more than submitting monthly or quarterly returns. In some businesses (particularly high-turnover businesses), the business has another mandatory requirement to file GSTR-9C, the GST Reconciliation Statement.
This form is a reconciliation between the GST returns submitted during the financial year and the audited financial statements of the taxpayer.
GSTR-9C ascertains financial information with the GST department as per the books of accounts. Any discrepancy needs to be reported and accounted for.
It is compulsory to file GSTR-9C if you are a business that is registered under GST, with a turnover of 5 crore every year. Many businesses use GST software to simplify this reconciliation and filing process.
This blog will discuss this process through the official GST portal.
What is GSTR-9C?
GSTR-9C is a self-certified form that reconciles GSTR-9 with the taxpayer’s audited financial statements for the financial year.
It was implemented on 13th September 2018 to promote transparency and accuracy in tax reporting. GSTR-9C previously had to be certified by a Chartered Accountant or Cost Accountant. And as of FY 202021, it merely needs to be self-certified by a taxpayer.
It’s like a GST audit report in which you have to justify any variation in sales, tax paid, or input tax credit (ITC) and give justification for the variation.
Who Needs to File GSTR-9C?
GSTR-9C is applicable to every GST-registered taxpayer whose aggregate turnover exceeds INR 5 crore in a financial year. It must be filed separately for each GSTIN under the same PAN.
However, certain taxpayers are exempt from filing GSTR-9C:
- Foreign airline companies complying with the Companies Act provisions
- Non-resident suppliers of OIDAR services to unregistered persons in India
- Taxpayers with aggregate turnover below INR 2 crore for FY 2023–24 (as per the 53rd GST Council meeting)
Due Date for Filing GSTR-9C
You should file GSTR-9C on the same date as GSTR-9. It should be filed on 31st December in the next year of the financial year. For example, the date of filing for the FY 2024-2025 is 31st December 2025.
GSTR-9C Format & Key Components
GSTR-9C is divided into two main parts. Part A focuses on reconciling GST returns with audited financial data, and Part B is a self-certification form.
Part A: Reconciliation Statement
This part compares the turnover, tax paid, and input tax credit (ITC) between the GST returns and the audited books of accounts. Since financial statements are prepared at the PAN level, taxpayers must extract and report details at the GSTIN level.
The reconciliation statement is divided into five main parts:
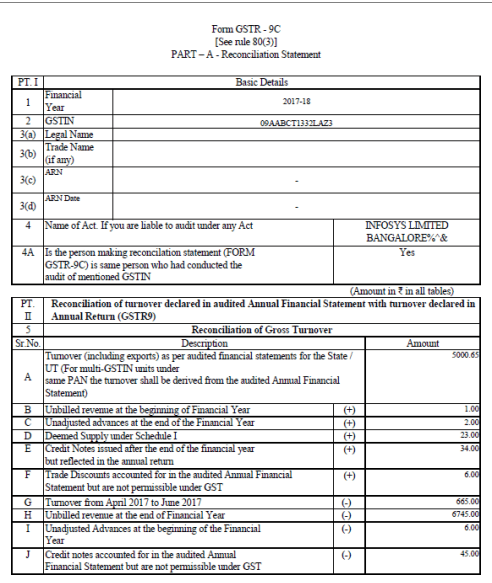
Part I – Basic Details
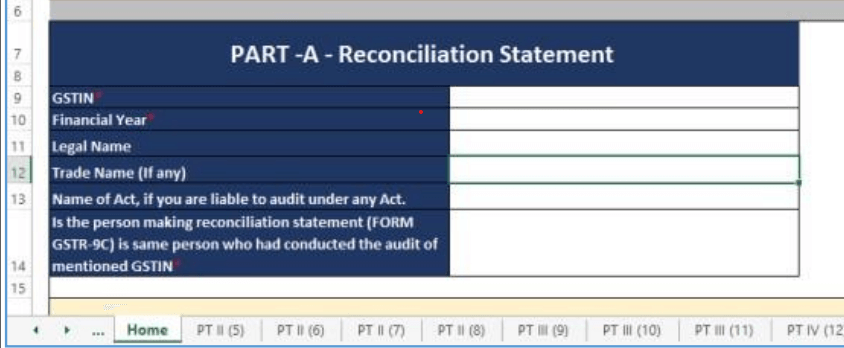
It captures:
- Financial Year (FY)
- GSTIN
- Legal Name and Trade Name of the taxpayer
- Whether audited under any other law
Part II – Turnover Reconciliation
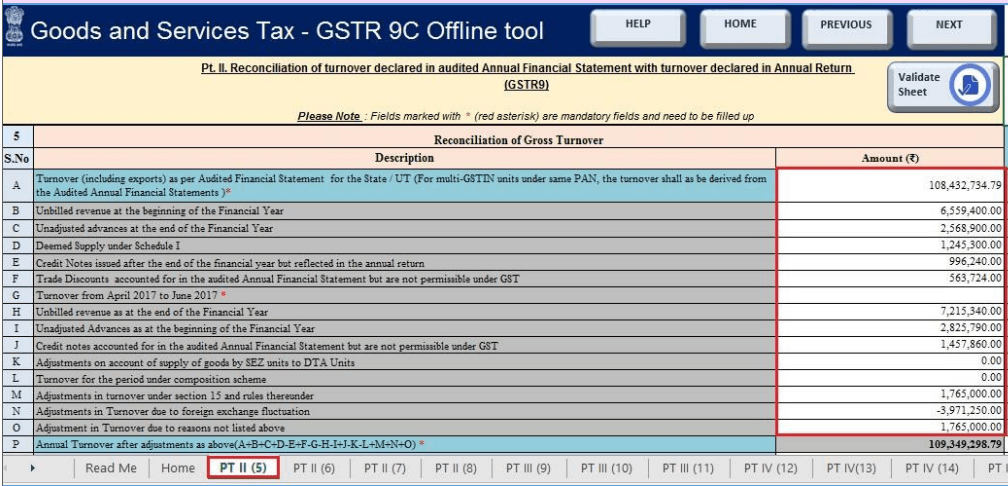
It compares:
- Gross and taxable turnover reported in GSTR-9
- Turnover declared in audited annual financial statements
Optional tables (5B to 5N) allow detailed adjustments, while Table 5O can be used for consolidated adjustments.
Tables 6 to 8 help explain any unreconciled figures and provide justification.
Part III – Reconciliation of Tax Paid
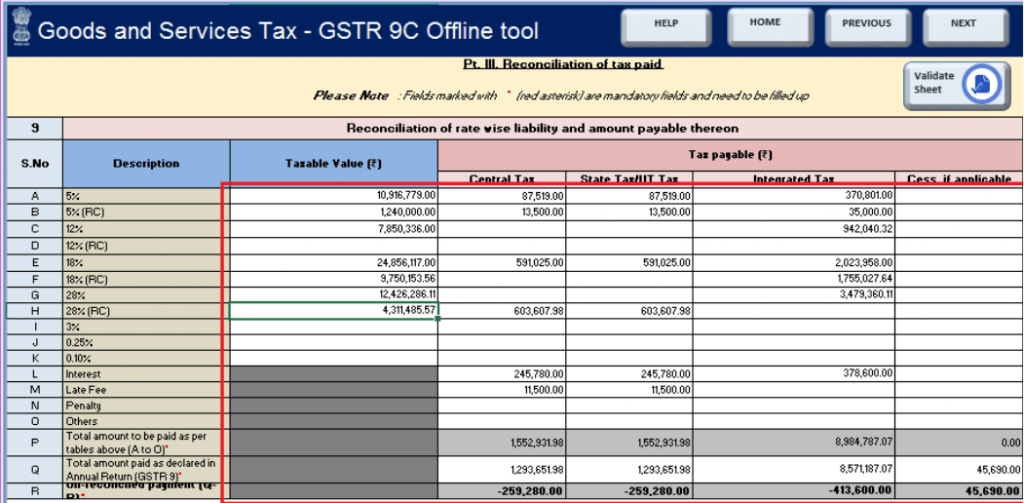
This section includes:
Table 9: Tax paid as per GSTR-9 vs. audited accounts, broken down by GST rate
Table 10: Reasons for any unreconciled amounts
Table 11: Additional liability, if any, identified during reconciliation
Part IV – Reconciliation of Input Tax Credit (ITC)
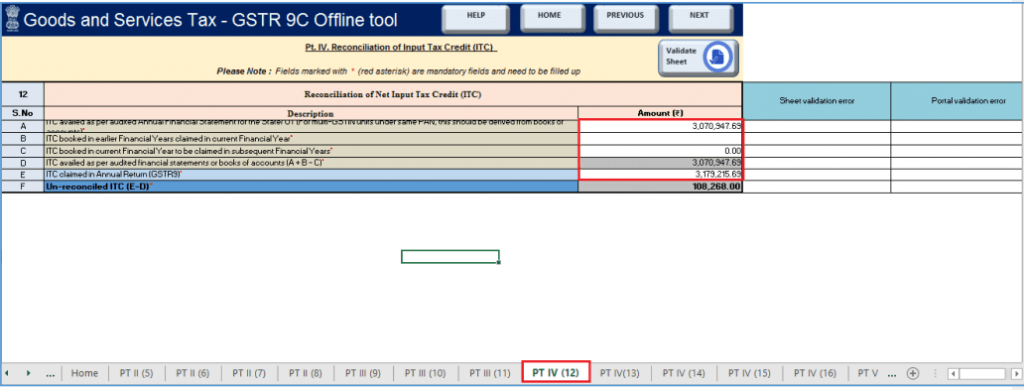
It focuses on:
- ITC availed as per GSTR-9 vs. ITC per the books of accounts
- Reporting of expenses with a split between eligible and ineligible ITC
- Reversals, if applicable
Optional tables such as 12B, 12C, and 14 make this section flexible for taxpayers.
Discrepancies, explanations, and payable differences are captured in Tables 13 to 16.
Part V – Additional Liability
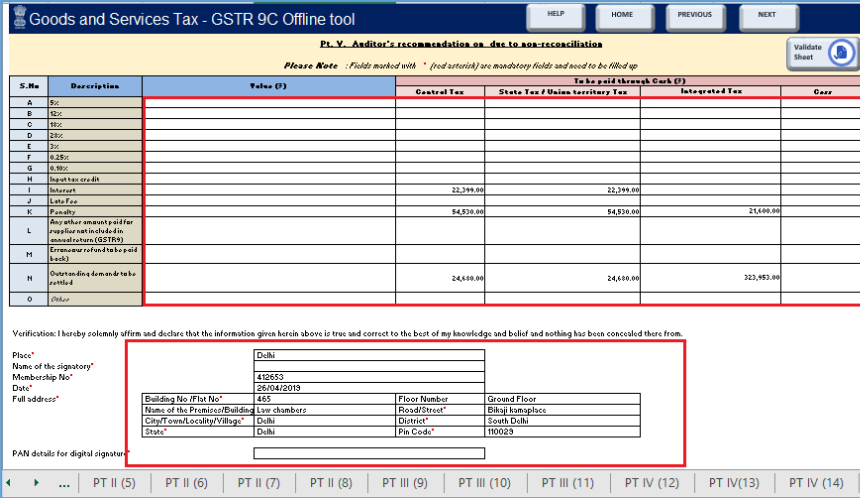
This part highlights:
- Liabilities due to non-reconciled turnover or ITC
- Any supplies not reported earlier
- Incorrect refund claims that need to be reversed
- Any outstanding GST dues
Taxpayers can pay the additional amount using FORM DRC-03 by selecting the Reconciliation Statement and using the electronic cash ledger.
Verification/Self-Certification
The last part of the form requires the GSTR-9C to be self-certified by the taxpayer. This may be through a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) or through an Aadhaar-based e-signature at the GST portal. A CA/CMA qualification is not required in FY 202021 and beyond.
Below, we have mentioned the format of the GSTR-9C form(preview of the first page):
Step-by-Step Guide: How to File GSTR-9C
The process of filing it might seem tough, but we have simplified it for you.
Before you move on to filing, you should check if you have filed GSTR-9 of the previous financial year or not. If yes, then only you can proceed to file GSTR-9C.
Let’s walk you through the guide.
What You Need Before Filing GSTR-9C
Make sure you have the following ready before you start filing GSTR-9C:
- Your GST portal login credentials
- A valid GSTIN (GST Identification Number)
- The filed GSTR-9 return for the relevant financial year
- Profit & Loss account, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow Statement
Step A: Login and Download Files from the GST Portal
- Visit the GST portal and log in.
- Click on the ‘Annual Return’ tab.
- Select the financial year you want to file GSTR-9C for.
- Download your filed GSTR-9 form.
- Download GSTR-9C tables derived from GSTR-9 (this pre-fills some data).
- Download the latest version of the GSTR-9C Offline Tool from the ‘Downloads’ section.
Step B: Prepare GSTR-9C Using the Offline Tool
This is where the actual preparation begins.
- Open the Excel-based GSTR-9C Offline Tool.
- Fill in table-wise details in the worksheet:
- Reconciliation of turnover (what you reported vs. what your books show)
- Taxes paid (based on different GST rates)
- Input Tax Credit claimed and utilized
- Additional liabilities identified through this reconciliation
- Once satisfied, click to generate a JSON file – this is the format you will upload to the portal.
- Use the Preview button to generate a PDF of your draft GSTR-9C and verify all information.

Kernel GST Billing Software
Starting Price
₹ 2999.00 excl. GST
Step C: Upload JSON File on the GST Portal
- Return to the GST portal.
- Upload the JSON file under the GSTR-9C section.
- If the portal detects any errors:
- Download the error report
- Correct the mistakes using the offline tool
- Generate and upload the corrected JSON file again
You can repeat this process until the file is accepted without errors.
Step D: Verify & File GSTR-9C
Once your JSON file is accepted and all data is correct:
- Review the form thoroughly one last time.
- Authenticate and file the return using:
- A Digital Signature Certificate (DSC), or
- An Aadhaar-based e-signature (if enabled)
After submission, download the filed copy for your records.
Step E: Pay Additional Tax Liability Using FORM DRC-03
Sometimes, during reconciliation, you may find that you owe additional GST due to:
- Underreported turnover
- Incorrect ITC claims
- Omitted supply of goods or services
In such cases:
- Navigate to ‘FORM DRC-03’ on the portal.
- Choose ‘Reconciliation Statement’ from the dropdown.
- Pay the additional tax using the electronic cash ledger only.
This ensures your GST compliance is fully settled.
Penalty for Late Filing of GSTR-9C
In case you fail to file the form before or on the due date, you have to pay a penalty.
Standard Penalty Structure
The penalty for late filing is:
- INR 100 per day under the CGST law
- INR 100 per day under SGST law
- That’s a total of INR 200 per day of delay.
However, there’s a cap on the total amount:
- The maximum penalty is 0.50% of your total annual turnover.
GSTR-9 vs GSTR-9C
Here’s a simplified comparison to help you differentiate between them:
| Feature | GSTR-9 | GSTR-9C |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Annual Return (Summary of the year’s GST activity) | Reconciliation Statement (GST data vs. audited accounts) |
| Applicability | For all regular GST-registered taxpayers | Mandatory only for taxpayers with a turnover of more than INR 5 crore |
| Certification | Self-signed by the taxpayer | Mandatory only for taxpayers with a turnover more than INR 5 crore |
| Late Fee | INR 200/day (maximum 0.25% of annual turnover) | INR 200/day (maximum 0.50% of annual turnover) |
| Financials Required | Not mandatory to attach audited financials | Audited financial statements must be submitted along with the return |
Final Checklist Before Filing GSTR-9C
- Review all GST returns (GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, GSTR-9) filed for the year
- Match your books of accounts with your GST filings
- Verify all input tax credit (ITC) claimed and utilized
- Report any discrepancy and pay additional liability via FORM DRC-03, where necessary
It is suggested to all businesses that they must stay informed to avoid compliance issues and penalties and maintain a clean record with the GST authorities.
FAQs
Is CA required for GSTR-9C?
No, you can file GSTR-9C without CA using the above guide. However, earlier it required a CA to verify and certify it, but now you can file it with self-certification only.
What happens if GSTR-9C is not filed?
In case you miss filing the GSTR-9C, you are imposed with a daily penalty of INR 200, of which INR 100 belongs to CGST and INR 100 to SGST. The upper cap stands at 0.5 per cent of turnover.
Who is eligible for GST 9C?
Any registered taxpayer (which has an aggregate annual turnover of more than INR 5 crore in one financial year) is required to file GSTR-9C.
Mehlika Bathla is a passionate content writer who turns complex tech ideas into simple words. For over 4 years in the tech industry, she has crafted helpful content like technical documentation, user guides, UX content, website content, social media copies, and SEO-driven blogs. She is highly skilled in... Read more