Proxmox vs VMware: Which Virtualization Platform Is Right for You?
Proxmox Virtual Environment (Proxmox VE) and VMware ESXi (vSphere) are two leading virtual servers. Each of these virtualization platforms caters to data center, private cloud, and enterprise virtualization workloads.
Both hyperconverged infrastructure solutions offer powerful features for running and managing virtual machines (VMs), but they differ fundamentally in licensing, technology stack, architecture, cost, and user experience.
Here’s a comprehensive comparison for those evaluating these platforms, including system administrators, small business IT professionals, enterprise architects, and infrastructure strategists.
Key Differences Between Proxmox and VMware
- Product Model & Licensing: Proxmox VE is an open-source tool with no licensing fees for using its core features. Its support subscriptions are optional. VMware ESXi is proprietary and requires paid licenses for enterprise features and centralized management.
- Virtualization Technologies: Proxmox supports both KVM/QEMU-based full virtualization and LXC containers. VMware uses its proprietary ESXi hypervisor and supports VMs natively. It uses Tanzu for Kubernetes container workflows.
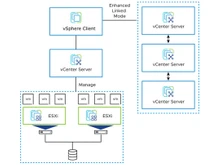
- Management Interface: Both platforms provide comprehensive web-based GUIs. Proxmox features a single-pane HTML5 interface for managing VMs, containers, storage, and networks. VMware uses the vSphere Client for advanced administration, with an ecosystem built around vCenter Server.
- Feature Set: Both systems offer clustering, high availability (HA), live migration, centralized multi-host management, and extensive hardware compatibility. VMware offers advanced enterprise features like Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), Fault Tolerance (FT), and vSAN. Proxmox provides integrated backups, Ceph/ZFS storage, and strong SDN support.
- Performance and Scalability: Proxmox is frequently cited for higher IOPS and lower latency on modern hardware. Whereas, VMware traditionally leads in host/cluster scaling and advanced workload optimization for massive enterprise deployments.
- Cost Structure: Proxmox is generally less expensive, especially for homelabs, testing, and small to mid-size deployments. VMware is a common choice for enterprises that require global support, integrations, and service-level agreements.
- Community vs. Enterprise Ecosystem: Proxmox has a vibrant open-source community, with rapid updates and direct access to platform internals. VMware has matured global partnerships and a long-standing professional support network.
VMware vs Proxmox VE Comparison Table
| Feature |
Proxmox VE |
VMware ESXi/vSphere |
| License & Cost |
Open source, free (paid support optional) |
Proprietary, subscription/license-based |
| Core Virtualization |
KVM (full), LXC (containers) |
ESXi hypervisor (full) |
| Container Support |
LXC native |
Via Tanzu w/ vSphere 7+ (Kubernetes pods) |
| Centralized Management |
Web UI & REST API, multi-master |
vCenter Server, vSphere Client |
| Clustering |
Yes, up to 32 hosts |
Yes, up to 96 hosts |
| HA & Live Migration |
Yes |
Yes, with advanced FT and DRS (Enterprise+) |
| Fault Tolerance |
No (HA only) |
Yes (FT) |
| Distributed Resource Scheduling |
No native DRS |
Yes, DRS |
| Storage Support |
Local, iSCSI, NFS, ZFS, Ceph |
Local, VMFS, vSAN, NFS, iSCSI |
| Max Hosts per Cluster |
32 |
96 |
| Max VMs per Host |
Unlimited |
1,024 |
| Max Physical Memory per Host |
12TB |
24TB |
| Backup & Snapshots |
vzdump, integrated backup server |
Extensive enterprise backup partners |
| OS & Hardware Support |
Windows, Linux, FreeBSD, Solaris; most hardware |
Windows, Linux, FreeBSD, macOS*, Solaris; extensive |
| Community/Support |
Open-source, paid optional |
Enterprise-grade, established |
| Pricing |
Free; €355/year for support |
Price on request |
Detailed Feature Comparison of VMware and Proxmox VE
Ease of Deployment & Administration
- Proxmox: It is an easy web-based installer that can be set up easily and start running in minutes. This virtualization platform has a unified interface for VMs and containers. It is ideal for sysadmins who like flexibility and transparency.
- VMware: It is a professional and polished installer with automation scripts and robust documentation. However, it consists of an additional learning curve for the full enterprise stack (vCenter, vSAN, NSX).
Virtualization & Containerization
- Proxmox: Natively supports both enterprise-grade VMs and lightweight Linux containers (LXC) in a single platform. Useful for density and dev/test environments.
- VMware: Focuses on robust full virtualization. Kubernetes integration is available with vSphere Tanzu for cloud-native container workloads, but requires higher licensing tiers.
Cost & Licensing
- Proxmox: No license fee for platform use. It is ideal for homelabs, education, and startups. Optional support packages are available with no feature lock-outs for free users.
- VMware: Requires a license for enterprise features, management, clustering, and support. Substantial investment for HA/DRS/FT and vendor support.
Performance & Scalability
- Proxmox: Recent benchmarks show 30-50% higher IOPS and lower latency than VMware ESXi under certain workloads. Best for agile environments demanding maximum open-source performance.
- VMware: Highly optimized for massive enterprise deployments, supporting more hosts and VMs per cluster and greater maximum RAM.
High Availability, Backup, and Disaster Recovery
- Proxmox: It has better HA clustering and supports failover for VMs and containers. Integrated vzdump backups and an optional backup server. No true “fault tolerance,” but good redundancy options.
- VMware: Industry-leading HA, plus Fault Tolerance (real-time VM mirroring), DRS for automated resource distribution, and an advanced backup ecosystem.
Storage & Networking
- Proxmox: ZFS, Ceph, local/LVM, and network storage (iSCSI, NFS). Full-featured SDN stack, granular networking and firewalling for containers and VMs.
- VMware: vSAN, VMFS, NFS, and deep integrations with physical SAN and NAS. NSX for SDN, superior for large-scale datacenter or hybrid cloud networking.
Community, Support, and Ecosystem
- Proxmox: Strong developer and user communities, rapid-release cycle, responsive to feature requests. Commercial-grade support is available, but optional.
- VMware: Mature professional ecosystem, wide 3rd-party integrations, certifications, and global professional support. Long track record in mission-critical enterprise settings.
When to Choose Proxmox or VMware?
| Use Case |
Recommended Platform |
| Open-source and budget-conscious deployments |
Proxmox |
| Homelab, dev/test, education |
Proxmox |
| Multi-tenant or hybrid VM/container workloads |
Proxmox |
| Seamless enterprise integrations, SLAs |
VMware |
| Environments requiring FT, DRS, vSAN |
VMware |
| Large enterprise/private cloud (>32 hosts) |
VMware |
| Environments leveraging vCenter ecosystem |
VMware |
Final Verdict: VMware or Proxmox?
Choose Proxmox if you want an open and cost-effective platform with robust hybrid VM/container support. Especially if you value transparency, SDN, and ZFS/Ceph, or are building a solution from the ground up, opt for Proxmox. If you require advanced clustering (FT, DRS), seamless enterprise integrations, and vendor-backed 24/7 support, especially in large-scale, production, or regulated environments, choose VMware.
Tip: For best results, lab both virtualization platforms using trial or free options, and use your use case, budget, and technical expertise as deciding factors.


 5 Ratings & 0 Reviews
5 Ratings & 0 Reviews