How to Improve Employee Motivation with Herzberg’s Two Factor Theory

What keeps your employees motivated? Is it the pay scale, job security or job satisfaction? Developing a workforce where employees get an appropriate source of motivation and a growing work environment often brings out their best performance.
A study conducted by the Association of American Psychology revealed that 89% of the total workforce at an organization would send good recommendations if there are engagement and wellness initiatives involved.
Additionally, engaged employees will deliver more productive work and result in 21 percent higher profitability. This is because empowered teams have lower desertion, and greater zeal to perform.
There are few popular theories that talk about the importance of employee motivation and its impact on overall productivity. Frederick Herzberg’s theory is one of the most frequently quoted theories by HR professionals. This article aims to explain Herzberg’s Two Factor theory in detail along with its implementation strategy.
What Is Herzberg’s Two Factor Theory?
Herzberg is an American psychologist, who turned into one of the most influential people in the world of management studies. He developed the Two-factor theory of motivation.
Frederick Herzberg’s two-factor theory says that a workplace consists of both negative and positive factors. Some factors lead to job satisfaction of employees and others lead to their dissatisfaction. He went to different organisations, ran multiple surveys and experiments, and finally drew the theory.
Herzberg Theory focused on three major factors i.e., employee’s attitude, motivation and overall job satisfaction.
The Two Factor Theory Is Based on Which Factors?
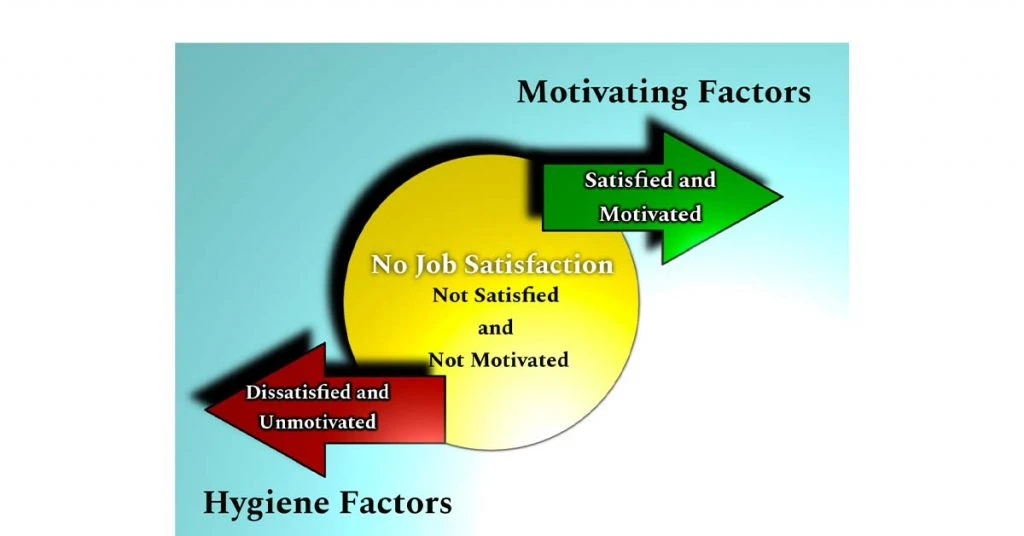
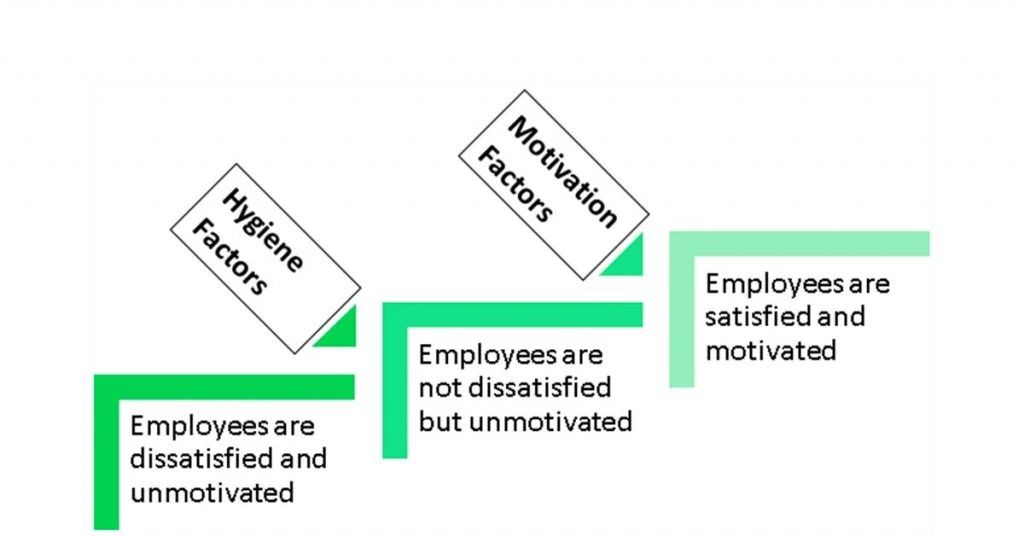
According to Herzberg’s Two Factor Theory of Motivation, the contrast of ‘Satisfaction’ is ‘No Satisfaction’ and the opposite of ‘Dissatisfaction’ is ‘No Dissatisfaction’. Herzberg 2 Factor Theory is further divided into two crucial factors: Hygienic and Motivational Factors.
What are Herzberg Hygiene Factors in the Workplace?
Those factors are essential to keep the employees motivated. However, they do not lead to long term satisfaction but the absence of these will lead to dissatisfaction at the workplace. The hygiene factors are also known as maintenance factors.
Herzberg’s Hygiene Factors (Factors of Satisfaction) represent the physiological needs that the employees want and look forward to being fulfilled. The negligence of which becomes a deal-breaker. Some of the popular Herzberg’s hygiene factors examples are:
Pay: Employees should not feel underpaid. The employee pay structure should match the market standards and must be equal to professionals working at the same level in the industry.
Job Security: Employees should trust the employer in order to deliver their best performance. The constant fear of getting fired will reduce their productivity.
Basic Benefits: They should get fringe benefits like health insurance covering their immediate family, EPF, leave policy, employee help policy, etc.
Company and Administrative Policies: The company policies should be comforting and not too harsh on employees. It should be fair to all and include flexibility for certain conditions. In the new normal, flexible working hours and hybrid work scenarios are crucial.
Physical working necessities: It is important to provide laptop and internet facilities for people working from home or office. You need to create decent working area with physical distance is quite important in the post pandemic world.
What are Motivational Factors in the Workplace?
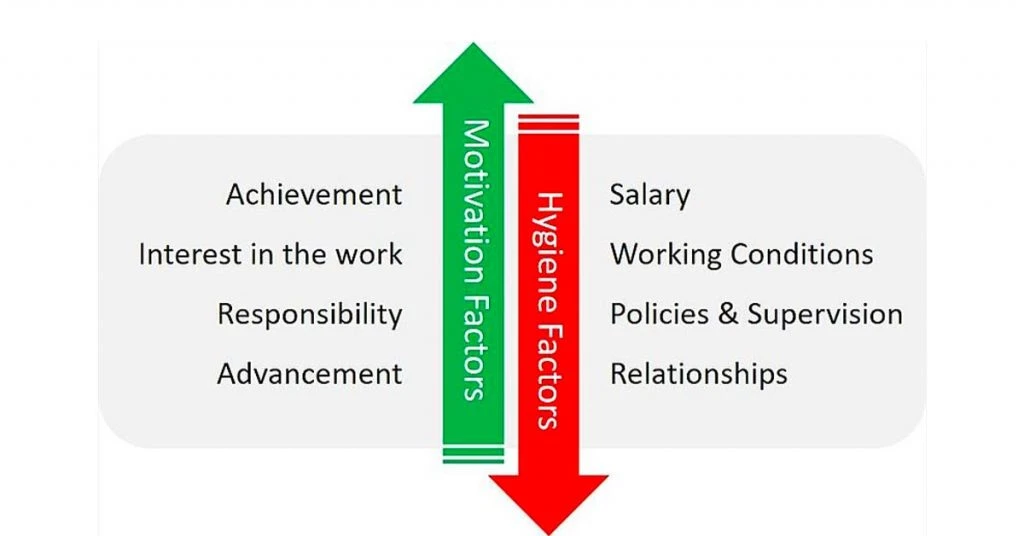
Unlike hygiene factors, Herzberg’s motivation theory highlights the ways to yield positive satisfaction in employees. Herzberg motivation factors are inherent to work and encourage employees to give a supreme performance. Therefore, these factors are also called satisfiers.
Herzberg’s two-factor theory of motivation are associated with the psychological needs of employees and they find these extremely rewarding. These factors include:
Promotion: Employees should not feel stuck in one job role and responsibilities over the year. The constant growth and promotional opportunities motivate them to perform well.
Rewards and Recognition: Employees need to be awarded and recognized by their senior managers for their exceptional contribution to work.
Futuristic: They always need something to look forward to. Employees should not feel myopic and always have a higher ambition to achieve.
Meaningfulness at work: The work itself should be meaningful and contribute to the growth of the organisation. The senior management should be full of energy that it becomes contagious to people reporting them.
Responsibility: Employees should hold full responsibility for their work. Whether it’s the fault at work or exceptional contribution, they should be held responsible.
Examples of Herzberg’s Two Factor Theory of Motivation
Herzberg’s 2 factor theory has been widely applied within organisations in studies to ensure staff satisfaction. One of the greatest examples is Ruthankoon and Ogunlana (2003), who tested Herzberg’s theory and extrapolated that different Herzberg motivation factors are functional in different disciplines in the Thai construction industry.
Tesco relies a lot on the elements of Frederick Herzberg two factor theory to ensure hygienic as well as motivational satisfaction for its employees. The company paid attention to factors causing dissatisfaction and satisfaction.
How to Apply Herzberg Theory of Motivation in the Workplace?
There are five ways to initiate the implication of Herzberg’s two factor theory of motivation at your workplace.
- Start from the Beginning
Make a list of job positions that are offering the least satisfaction to employees. You need to figure out the areas where performance can be improved, and roles and responsibilities can be defined for a higher level of satisfaction.
- Listen to Them
Reach out to the departments that are under performing. Sit with department heads and respective employees and ask specific questions about problem areas, accomplishments, training, recognitions etc. If your employee engagement and surveys are poor, take specific actions.
- Judge Every Performance
Your employees are the biggest asset for your company. If an asset is becoming a liability for you, you need to take action. Your company is as good as your well performing employees. Do not let the high standards sink.
- Give them Autonomy
The more employees feel responsible for competition of task, the greater will be their sense of achievement. Autonomy is one of the biggest factors of motivation. The employer needs to make their employees take ownership of their work which eventually will empower the organisation.
- Evaluate Regularly
Supervisors should get the right balance of feedback through one-on-one calls, mentoring sessions, reviews to set a track leading to achieving the said goal. A healthy relationship between workers and their managers will increase productivity, improve quality, and ensure clear communication.
- Take Care of the Resources
Give them the opportunity to fly, let them achieve more and challenge themselves. However, it’s your responsibility to ensure they have the tools, resources, skills and information to fulfil the job.
- Improve Working Environment
After suffering from the hazardous situation of the global pandemic, every employee will need a workplace that follows every covid protocol. Employers also need to tailor the working policies depending on the current situation. Always remember low hygiene is equal to low employee motivation.
- Take a Macro Look at Employee Interest
Herzberg’s Two Factor Theory states that employers cannot pick one between hygiene and motivation. They need to strive to achieve the best of both. When it comes to job factors employers need to take a look at the wider array of employee needs.
Conclusion
There are multiple theories of motivation that managers can attempt to implement at the workplace. However, Herzberg’s two-factor theory has been implemented by most successful organisations today. Improving both hygiene factors and motivation factors helps organizations groom a productive and motivated workforce.
If the senior level management implements the theory correctly, it can boost employee concentration, improve productivity, and reduce attrition.
Herzberg Two Factor Theory addresses how employee motivation is impacted by different elements of satisfaction and dissatisfaction. By investing time to understand your employees, and implementing a few policy changes, you can greatly improve employee motivation.
FAQs
What is Herzberg's two-factor theory of job satisfaction?
Herzberg's two-factor theory is a psychological theory of motivation in a workplace. It states that in the workplace certain factors lead to satisfaction and some factors lead to dissatisfaction.
Therefore, Herzberg segregated the factors into two categories; Hygiene and Motivational factors to ensure motivation at work.What are the two factors in Herzberg's two-factor theory?
Two factors in Herzberg's two-factor theory are Hygienic factors and Motivational factors. Having a work environment with high hygiene to keep your employees away from matters of dissatisfaction is crucial.
On the other hand, factors that give the employees motivation to work with a great sense of purpose and significance are Motivational factors like Promotion, Rewards and Recognition, Responsibility etc.What is Herzberg's theory of motivation in the workplace?
Just like the name suggests, Herzberg's theory of motivation talks about the factors that result in higher employee satisfaction. As per the theory, there are a few psychological needs that employees find extremely rewarding. Such as meaningfulness at work, having a futuristic approach, promotion, and recognition at work, etc.
What are Herzberg's motivation factors?
Herzberg's motivation factors are related to inherent work factors that keep the employee motivated. According to Herzberg's Theory, promotion, reward and recognition, relevancy of work, and accountability are primary motivators.
Why is Herzberg's theory important?
Herzberg's 2-factor theory helps managers understand the workplace's major factors as satisfiers and dissatisfiers. Identifying and improving the hygiene and motivation factors allows businesses to retain top talent and increase productivity.
What are the differences between Herzberg's motivational and maintenance factors?
The absence of maintenance (hygiene) factors dissatisfies the employee; however, their presence doesn't satisfy the employee. Example: Salary, health benefits, relationship with the employer. While motivational factors like promotions, rewards, etc., satisfy the employees, their absence doesn't dissatisfy the employee.
Who proposed the two-factor theory?
American psychologist Frederick Herzberg proposed the two-factor theory of motivation. This theory mentions the two major factors: Hygiene and Motivation, that affect the long-term job satisfaction of employees.
The Techjockey content team is a passionate group of writers and editors dedicated to helping businesses make informed software buying decisions. We have a deep understanding of the Indian software market and the challenges that businesses face when choosing the right software for their needs. We are committed... Read more